Body lice
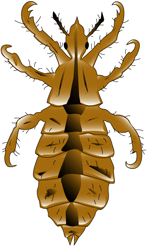
Body lice are parasitic insects that live on clothing and bedding used by infested persons. They feed on blood and usually move to their host's body for that purpose only. Body lice are generally longer than head lice but the 2 types look very similar despite their difference in size.
Body lice cause intense itching which is usually worse around the shoulders, the abdomen and the buttocks. Bites may also appear as small red spots.
Unlike head lice, body lice can transmit serious infections, which is why it is important to eliminate the problem as quickly as possible.
Causes and triggers
Body lice are transmitted from person to person through shared use of infested clothing and bedding. Lice lay their eggs on clothing fibres, most often along the seams, though sometimes the eggs can also stick to body hair.
Body lice are most often found among individuals with poor hygiene or those living in crowded conditions.
Treatment
Body lice can most likely be prevented and eradicated by washing on a regular basis and changing clothes and bedding at least once a week. Swapping clothes is not recommended.
Washing clothing in hot water and drying them on the hottest setting will help kill most of the lice embedded in clothing and bedding. Objects that cannot be cleaned that way should be dry-cleaned or put in a sealed plastic bag for 2 weeks.
A treatment against lice is generally not necessary if hygiene is maintained and items are appropriately laundered at least once a week.
For more information, do not hesitate to speak to your health care provider.